一、 概述
Java 中的网络支持:
InetAddress:用于表示网络上的硬件资源,即 IP 地址;URL:统一资源定位符;Sockets:使用 TCP 协议实现网络通信;Datagram:使用 UDP 协议实现网络通信。
二、 InetAddress
没有公有的构造函数,只能通过静态方法来创建实例。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
public class IPTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException {
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
System.out.println(address.getHostAddress());
System.out.println(address.getHostName());
address = InetAddress.getByName("www.163.com");
System.out.println(address.getHostAddress());
System.out.println(address.getHostName());
address = InetAddress.getByName("183.216.182.7");
System.out.println(address.getHostAddress());
System.out.println(address.getHostName());
}
}
|
端口
ip地址用来标识一台计算机,端口用来区分不同的程序。
常用的命令:
查看所有端口: netstat -ano
查看指定端口: netstat -ano | findstr “5023”
查看指定进程: tasklist | findstr “5032”
查看具体程序: 使用任务管理器查看pid
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
InetSocketAddress socketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",8080);
InetSocketAddress socketAddress2 = new InetSocketAddress("localhost",9000);
System.out.println(socketAddress.getHostName());
System.out.println(socketAddress2.getAddress());
System.out.println(socketAddress.getPort());
|
三、 URL
URL(Uniform Resource Locator): 统一资源定位符 , 由4部分组成:协议 、存放资源的主机域名、端口号和资源文件名。 如: http://www.www.baidu.com:9090/index.html
URL是指向互联网“资源”的指针。资源可以是简单的文件或目录,也可以是对更为复杂的对象的引用,例如对数据库或搜索引 擎的查询。
互联网的三大基石: html, http, url
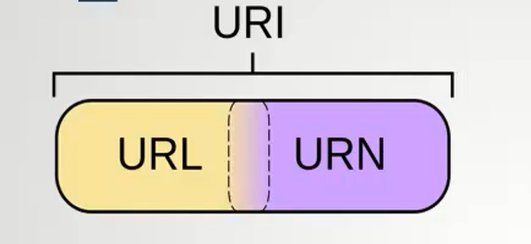
URI(Universal Resource Identifier): 统一资源标志符,用来标识抽象或者物理资源的一个紧凑字符串。
URN(Universal Resource Name):统一资源名称, 通过特定命名空间中的唯一名称或ID来标识资源。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
public class URLTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws MalformedURLException {
URL url = new URL("http://www.baidu.com:9090/index.html?uname=zhu&age=18#a");
System.out.println("协议:"+ url.getProtocol());
System.out.println("域名|ip: "+ url.getHost());
System.out.println("请求的资源1:"+ url.getFile());
System.out.println("请求的资源2: "+ url.getPath());
System.out.println("参数:"+ url.getQuery());
System.out.println("锚点: "+ url.getRef());
}
}
|
协议:http
域名|ip: www.baidu.com
请求的资源1:/index.html?uname=zhu&age=18
请求的资源2: /index.html
参数:uname=zhu&age=18
锚点: a
爬虫原理
使用url来下载资源
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.URL;
public class SpyderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
URL url = new URL("https://www.jd.com");
InputStream is = url.openStream();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is, "utf8"));
String msg = null;
while(null != (msg=br.readLine())){
System.out.println(msg);
}
br.close();
}
}
|
对于不能直接通过URL来获取资源的,可以通过浏览器请求方式来获取:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
public class SpyderTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
URL url = new URL("https://www.dianping.com");
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection)url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("GET");
conn.setRequestProperty("User-Agent", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/80.0.3987.106 Safari/537.36");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(conn.getInputStream(), "utf8"));
String msg = null;
while (null != (msg = br.readLine())){
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
}
|
四、 传输协议TCP&UDP
TCP
传输控制协议 TCP(Transmission Control Protocol)是面向连接的,提供可靠交付,有流量控制,拥塞控制,提供全双工通信,面向字节流(把应用层传下来的报文看成字节流,把字节流组织成大小不等的数据块),每一条 TCP 连接只能是点对点的(一对一)。
UDP
用户数据报协议 UDP(User Datagram Protocol)是无连接的,尽最大可能交付,没有拥塞控制,面向报文(对于应用程序传下来的报文不合并也不拆分,只是添加 UDP 首部),支持一对一、一对多、多对一和多对多的交互通信。
套接字Socket
我们开发的网络应用程序位于应用层,TCP和UDP属于传输层协议,在应用层如何使用传输层 的服务呢?在应用层和传输层之间,则是使用套接字来进行分离。
套接字就像是传输层为应用层开的一个小口,应用程序通过这个小口向远程发送数据,或者 接收远程发来的数据;而这个小口以内,也就是数据进入这个口之后,或者数据从这个口出来之前,是不知道也不需要知道的,也不会关心它如何传输,这属于网络其它层次的工作。
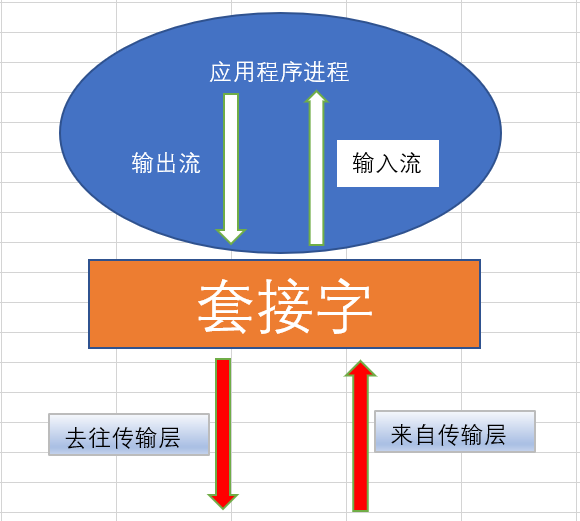
Socket实际是网络传输层供给应用层的编程接口。传输层则在网络层的基础上提供进 程到进程问的逻辑通道,而应用层的进程则利用传输层向另一台主机的某一进程通 信。Socket就是应用层与传输层之间的桥梁 。
使用Socket编程可以开发客户机和服务器应用程序,可以在本地网络上进行通信,也 可通过Internet在全球范围内通信。
生活案例1:
如果你想写封邮件发给远方的朋友,如何写信、将信 打包,属于应用层。信怎么写,怎么打包完全由我们做主;
而当我们将信投入邮筒时,邮筒的那个口就是套接字, 在进入套接字之后,就是传输层、网络层等(邮局、公路交管或者航线等)其它层次的工作了。我们从来不会去关心信是如何从西安发往北京的,我们只知道 写好了投入邮筒就OK了。

生活案例2:
如果你想发货给国外,你只要把 货物放入集装箱,然后交给码头就可以了。发送什么货物,货物如何打包, 完全有你做主。 码头就是套接字,剩下的事情就 交给港口和货运公司处理就行了,具体细节我们无需了解。

五、 UDP编程
Datagram
- DatagramSocket:通信类 : 用于发送或者接受数据包的套接字
- DatagramPacket:数据包类
使用基于UDP协议的Socket网络编程实现 :
不需要利用IO流实现数据的传输。 每个数据发送单元被统一封装成数据包的方式,发送方将数据包发送到网络中,数据包在网络中去寻找他的目的地。
UDP编程 : 一切转换成字节数组
接收端:
1.使用DatagramSocket 指定端口 创建接收端
2.指定容器, 封装DatagramPacket包
3.阻塞式接受包裹receive(DatagramPacket p)
4.分析数据 byte[] getData() getLength()
5.释放资源
发送端
1.使用DatagramSocket 指定端口 创建发送端
2.准备数据 ==》 一定要转成字节数组
3.封装 DatagramPacket包,需要指定目的地 + 端口
4.发送包裹 send( DatagramPacket p)
5.释放资源
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
public class UDPServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("接收端启动中...");
DatagramSocket server = new DatagramSocket(8888);
byte[] contiainer = new byte[1024*60];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(contiainer, 0, contiainer.length);
server.receive(packet);
byte[] datas = packet.getData();
int len = packet.getLength();
System.out.println(new String(datas, 0, len));
server.close();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
public class UPDCilent {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("发送方启动中...");
DatagramSocket client = new DatagramSocket(9999);
String data = "Hello world";
byte[] datas = data.getBytes();
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(datas, 0, datas.length,
new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8888));
client.send(packet);
client.close();
}
}
|
UDP编程: 传输基本数据类型和引用
服务端(接收端):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
public class UDPTypeServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("传输基本数据类型==>接收端启动中。。。。");
DatagramSocket server = new DatagramSocket(9898);
byte[] datas = new byte[1024*90];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(datas, 0, datas.length);
server.receive(packet);
byte[] data = packet.getData();
int len = packet.getLength();
ObjectInputStream dis = new ObjectInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(data)));
String msg = dis.readUTF();
boolean flag = dis.readBoolean();
int a = dis.readInt();
Object o = dis.readObject();
System.out.println(len);
System.out.println(a+"=>"+msg+"-->"+flag);
if(o instanceof Employee){
Employee e = (Employee)o;
e.toString();
System.out.println("的确是马云");
System.out.println(e.getName() +":"+ e.getMoney());
}
server.close();
}
}
|
客户端(发送端):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
public class UPDTypeCilent {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("传输基本数据类型==>发送方启动中...");
DatagramSocket client = new DatagramSocket(9999);
ByteArrayOutputStream bao = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream dos = new ObjectOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(bao));
dos.writeUTF("Hello world!");
dos.writeBoolean(true);
dos.writeInt(99);
Employee e = new Employee("马云", 900000);
dos.writeObject(e);
dos.flush();
byte[] datas = bao.toByteArray();
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(datas, 0, datas.length,
new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 9898));
client.send(packet);
client.close();
}
}
|
传输基本数据类型==>发送方启动中…
66
99=>Hello world!–>true
的确是马云
null:900000.0
UDP编程: 传输文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| import java.io.*;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
public class UPDFileCilent {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("文件 ==> 发送方启动中...");
DatagramSocket client = new DatagramSocket(9999);
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("./socket/socket.png");
BufferedInputStream bi = new BufferedInputStream(is);
ByteArrayOutputStream os = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] data = new byte[1024*60];
int len;
while ( -1 != (len = is.read(data,0, data.length))){
os.write(data, 0, len);
os.flush();
}
byte[] datas = os.toByteArray();
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(datas, 0, datas.length,
new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8888));
client.send(packet);
client.close();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
public class UDPFileServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("接收端启动中...");
DatagramSocket server = new DatagramSocket(8888);
byte[] contiainer = new byte[1024*60];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(contiainer, 0, contiainer.length);
server.receive(packet);
byte[] datas = packet.getData();
int len = packet.getLength();
BufferedOutputStream os =new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("./socket/copy.png"));
os.write(datas, 0, datas.length);
os.flush();
server.close();
}
}
|
UDP案例: 多线程实现在线咨询
发送端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.SocketException;
public class talkSend implements Runnable {
private DatagramSocket client ;
private BufferedReader reader;
private String toIP;
private int toPort;
public talkSend(int port, String toIP, int toPort) {
this.toIP = toIP;
this.toPort = toPort;
try {
this.client = new DatagramSocket(port);
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
} catch (SocketException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
String msg = null;
try {
msg = reader.readLine();
byte[] datas = msg.getBytes();
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(datas, 0, datas.length, new InetSocketAddress(this.toIP, this.toPort));
client.send(packet);
if("bye".equals(msg)){
break;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
client.close();
}
}
|
接收端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.SocketException;
public class talkRecieve implements Runnable{
private DatagramSocket server;
public talkRecieve(int port) {
try {
this.server = new DatagramSocket(port);
} catch (SocketException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
byte[] data = new byte[1024*60];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(data,0, data.length);
try {
server.receive(packet);
byte[] datas = packet.getData();
String msg = new String(datas);
System.out.println(msg);
if ("bye".equals(msg)){
break;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
server.close();
}
}
|
创建学生端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public class TalkStudent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new talkSend(8989, "localhost", 9999)).start();
new Thread(new talkRecieve(10024)).start();
}
}
|
创建教师端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public class TalkTeacher {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new talkRecieve(9999)).start();
new Thread(new talkSend(10025, "localhost", 10024)).start();
}
}
|
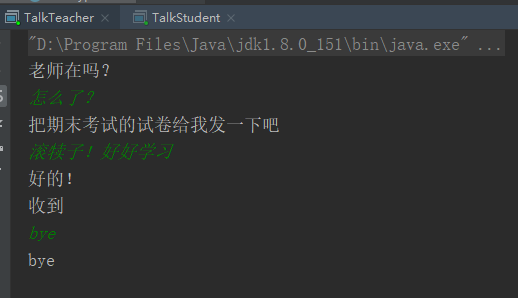
六、 TCP 编程
TCP协议基于请求-响应模式, 在网络通讯中,第一次主动发起通讯的程序被称作客户端(Client)程序,第一次通讯中等待连接的程序被称作服务器端 (Server)程序。利用IO流实现数据的传输。
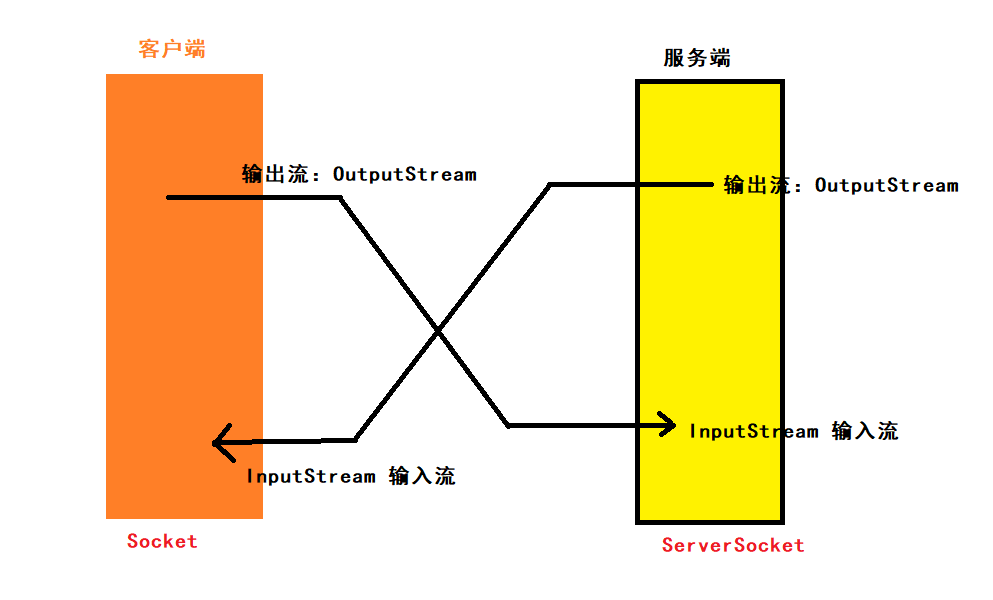
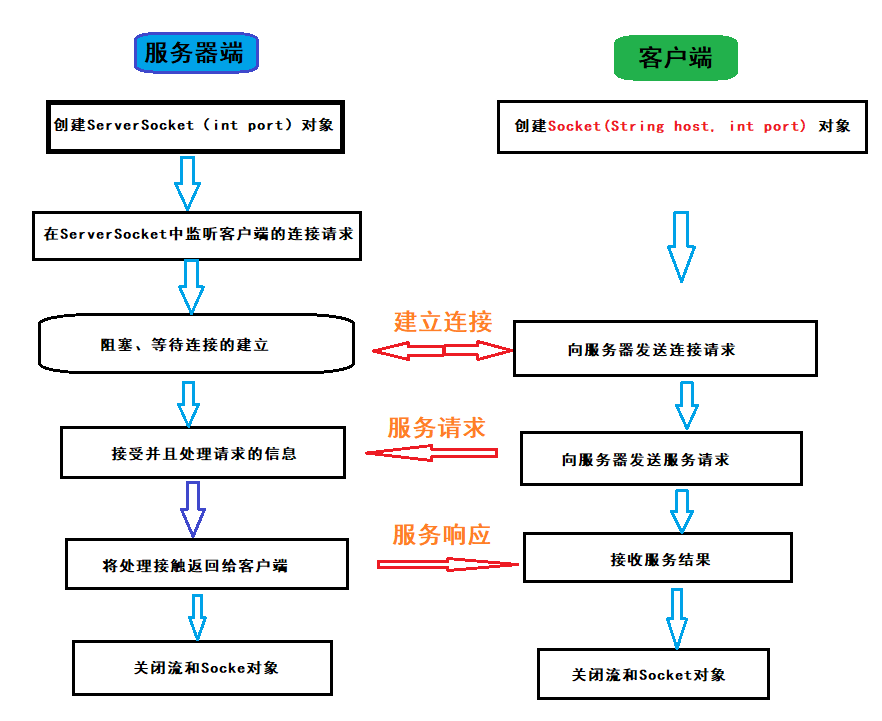
TCP通信原理
服务器创建ServerSocket,在指定端口监听并并处理请求。
客户端创建Socket,向服务器发送请求。
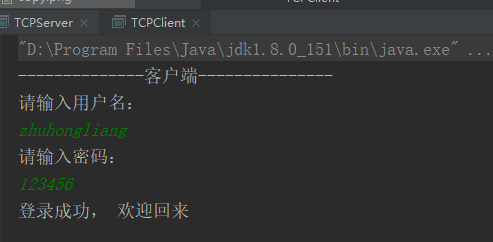
完成网络登录功能
使用基于TCP协议的Socket网络编程实现。
单向:客户端向服务器端发送字符串,服务器获取字符串并输出
双向:服务器端给出客户端反馈,客户端得到反馈并输出
对象:客户端向服务器端发送User对象,服务器端获取对象并输出
多线程:服务器接收多个客户端的请求,并给出反馈每个客户请求开启一个线程
服务端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* TCP单向: 服务端
* @author Hongliang Zhu
* @create 2020-02-21 13:28
*/
public class TCPServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
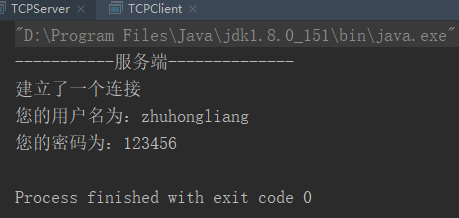
System.out.println("-----------服务端--------------");
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(9696);
Socket cilent = server.accept(); // 监听连接请求, 返回对应的客户端
System.out.println("建立了一个连接");
InputStream is = cilent.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);
// 读取
String uname = null;
String upwd = null;
String msg = dis.readUTF();
String []datas = msg.split("&");
for(String s: datas){
String[] info = s.split("=");
if("uname".equals(info[0])){
System.out.println("您的用户名为:"+ info[1]);
uname = info[1];
}
if("upwd".equals(info[0])){
System.out.println("您的密码为:"+ info[1]);
upwd = info[1];
}
}
//判断:返回给客户端的信息
String back = null;
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(cilent.getOutputStream());
if("zhuhongliang".equals(uname) && "123456".equals(upwd)){
back = "登录成功, 欢迎回来";
}else{
back = "用户名或者密码错误!";
}
dos.writeUTF(back);
dos.flush();
// 关闭资源
dos.close();
dis.close();
cilent.close();
}
}
|
客户端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| import java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
public class TCPClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
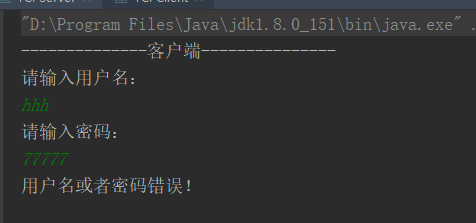
System.out.println("--------------客户端---------------");
Socket client = new Socket("localhost", 9696);
String uname;
String upwd;
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
uname = br.readLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
upwd = br.readLine();
String msg = "uname="+ uname +"&"+"upwd="+upwd;
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream());
dos.writeUTF(msg);
dos.flush();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream());
String res = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println(res);
dos.close();
br.close();
client.close();
}
}
|
文件上传
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| import java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
public class FileClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("--------------客户端---------------");
Socket client = new Socket("localhost", 9696);
InputStream is = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("./io/io.png"));
OutputStream os = new BufferedOutputStream(client.getOutputStream());
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
while (-1 != (len = is.read(buff))){
os.write(buff,0, len);
}
os.flush();
os.close();
is.close();
client.close();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class FileServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("-----------服务端--------------");
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(9696);
Socket cilent = server.accept();
System.out.println("建立了一个连接");
InputStream is = new BufferedInputStream(cilent.getInputStream());
OutputStream os = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("./socket/tcp.png")));
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
while (-1 != (len = is.read(buff))){
os.write(buff,0, len);
}
os.flush();
is.close();
os.close();
cilent.close();
}
}
|
多用户登录
服务端: 使用了多线程实现多个用户同时处理,将对接管道封装
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
| import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class TCPMutiServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("-----------服务端--------------");
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(9696);
boolean isRuning = true;
while (isRuning){
Socket cilent = server.accept();
System.out.println("建立了一个连接");
new Thread(new Channel(cilent)).start();
}
}
static class Channel implements Runnable{
private Socket client;
private DataInputStream dis;
private DataOutputStream dos;
public Channel(Socket client){
this.client = client;
try {
dis = new DataInputStream(this.client.getInputStream());
dos = new DataOutputStream(this.client.getOutputStream());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public String recieve(){
String msg = "";
try {
msg = dis.readUTF();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return msg;
}
private void send(String msg){
try {
dos.writeUTF(msg);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void release(){
try {
if (null != dos)
dos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (null != dis)
dis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (null != client)
client.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
String msg = recieve();
String uname = null;
String upwd = null;
String []datas = msg.split("&");
for(String s: datas){
String[] info = s.split("=");
if("uname".equals(info[0])){
System.out.println("您的用户名为:"+ info[1]);
uname = info[1];
}
if("upwd".equals(info[0])){
System.out.println("您的密码为:"+ info[1]);
upwd = info[1];
}
}
String back = null;
if("zhuhongliang".equals(uname) && "123456".equals(upwd)){
back = "登录成功, 欢迎回来";
}else{
back = "用户名或者密码错误!";
}
send(back);
release();
}
}
}
|
客户端: 对发送和接受高度封装:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
| import java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
public class TCPMultiClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("--------------客户端---------------");
Socket client = new Socket("localhost", 9696);
new Send(client).send();
new Recieve(client).recieve();
}
static class Send{
private Socket client;
private BufferedReader br;
private DataOutputStream dos;
String msg = "";
public Send(Socket client){
this.client = client;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
dos = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream());
msg = init();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private String init(){
String uname = "";
String upwd = "";
try {
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
uname = br.readLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
upwd = br.readLine();
return "uname="+ uname +"&"+"upwd="+upwd;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "";
}
private void send(){
try {
dos.writeUTF(msg);
dos.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
static class Recieve{
private Socket client;
private DataInputStream dis;
public Recieve(Socket client) {
this.client = client;
try {
dis = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void recieve(){
try {
String res = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println(res);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
|
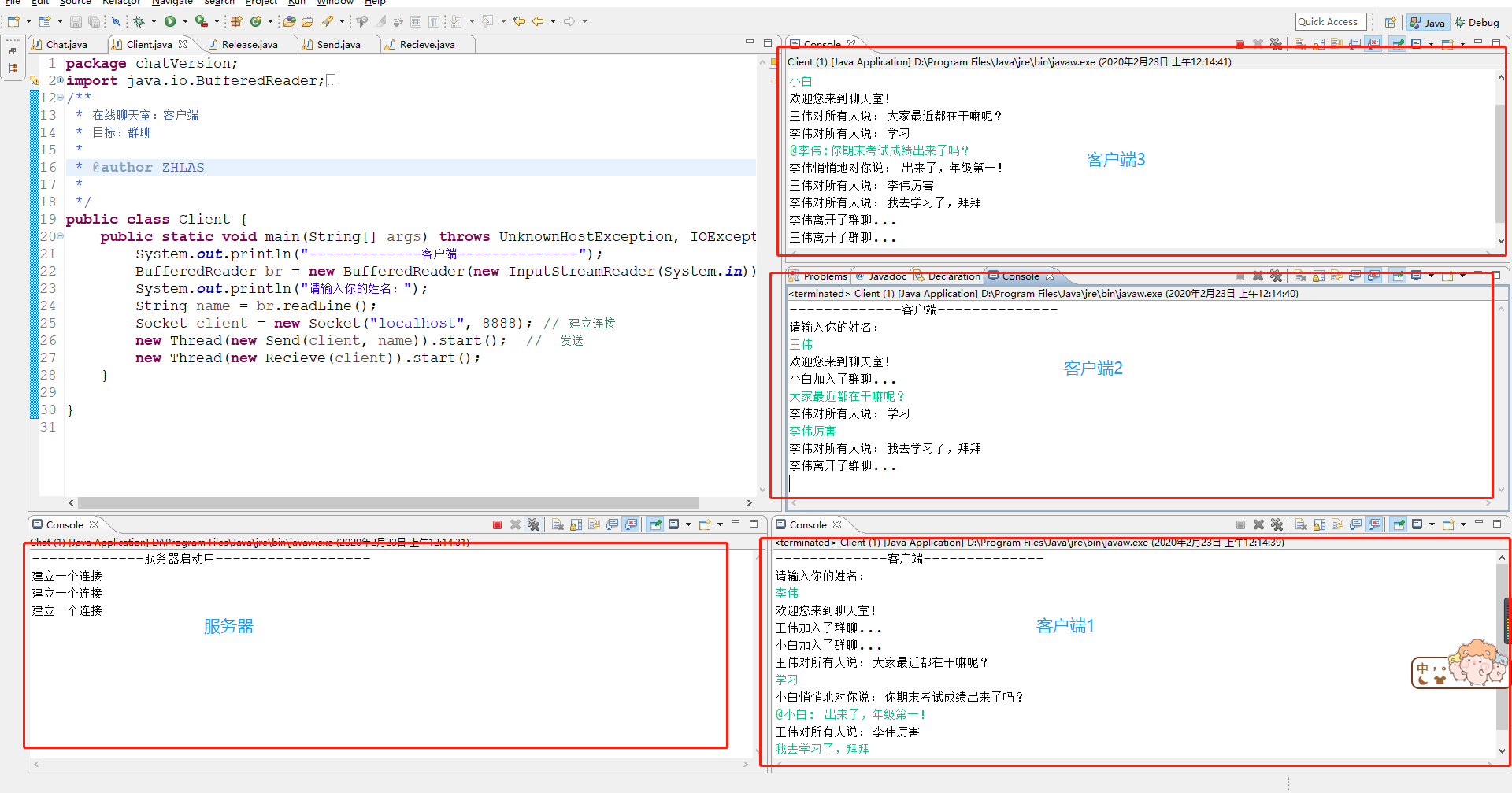
七、 实例: 手写在线聊天室
1. 服务器
功能:相当于消息的中转站(转发器)
1.可以同时处理多个客户端的请求。
2.当一个用户进入群聊的时候,会给群聊中所有的用户群发一条系统消息,提示所有用户有人进来了群聊当中。
3.当一个用户成功进入群聊的时候, 服务器会发送一条问候语给当前客户。
4.当一个用户离开群聊的时候,会给群聊中所有的用户群发一条系统消息,提示所有用户xxx离开了群聊。
5.一个用户发送的消息可以给群聊中的所有用户发送。
6.可以对指定的用户私聊,消息只对指定的用户看见。格式: @xxx:message
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
| package chatVersion;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;
import javax.management.relation.Relation;
import javax.print.attribute.standard.MediaSize.Other;
public class Chat {
static CopyOnWriteArrayList<Channel> all = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("-------------服务器启动中------------------");
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8888);
while(true){
Socket client = server.accept();
System.out.println("建立一个连接");
Channel c = new Channel(client);
all.add(c);
new Thread(c).start();
}
}
static class Channel implements Runnable{
private Socket client;
private DataInputStream dis = null;
private DataOutputStream dos = null;
private boolean isRuning = true;
private String name;
public Channel(Socket client) {
this.client = client;
try{
dis = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream());
dos= new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream());
this.name = recieve();
this.send("欢迎您来到聊天室!");
sendOthers(this.name+ "加入了群聊...", true);
}catch(Exception e){
relese();
}
}
private String recieve() {
String msg = "";
try {
msg = dis.readUTF();
} catch (IOException e) {
relese();
}
return msg;
}
private void send(String msg) {
try {
dos.writeUTF(msg);
} catch (IOException e) {
relese();
}
}
private void sendOthers(String msg, boolean isSys) {
boolean isPrivate = msg.startsWith("@");
if(isPrivate){
int idx = msg.indexOf(":");
String targetName = msg.substring(1, idx);
msg = msg.substring(idx+1);
for(Channel target : all){
if(target.name.equals(targetName)){
target.send(this.name +"悄悄地对你说: "+msg);
}
}
}else{
for(Channel c: all){
if(this == c){
continue;
}else{
if(!isSys)
c.send(this.name+"对所有人说: "+msg);
else
c.send(msg);
}
}
}
}
private void relese(){
this.isRuning = false;
Release.reslese(dos, dis, client);
all.remove(this);
sendOthers(this.name+"离开了群聊...", true);
}
public void run() {
String msg ="";
while(isRuning){
msg = recieve();
if(!"".equals(msg)){
sendOthers(msg, false);
}
}
}
}
}
|
2. 客户端
功能:
1.发送消息给服务器
2.从服务器那边接收消息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| package chatVersion;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import java.nio.Buffer;
import org.omg.CosNaming.NamingContextExtPackage.StringNameHelper;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException, IOException {
System.out.println("-------------客户端--------------");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("请输入你的姓名:");
String name = br.readLine();
Socket client = new Socket("localhost", 8888);
new Thread(new Send(client, name)).start();
new Thread(new Recieve(client)).start();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| package chatVersion;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Send implements Runnable{
private Socket client;
private BufferedReader br;
private DataOutputStream dos;
private boolean isRuning = true;
private String name;
public Send(Socket client, String name) {
this.client = client;
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
this.name = name;
try {
dos = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream());
send(name);
} catch (IOException e) {
this.isRuning = false;
Release.reslese(dos, br, client);
}
}
private void send(String msg) {
try {
dos.writeUTF(msg);
dos.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
this.isRuning = false;
Release.reslese(dos, br);
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(isRuning){
String msg = "";
try {
msg = br.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
this.isRuning = false;
Release.reslese(br);
}
send(msg);
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| package chatVersion;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Recieve implements Runnable{
private Socket client;
private DataInputStream dis;
private boolean isRuning = true;
public Recieve(Socket client) {
this.client = client;
try {
dis = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream());
} catch (IOException e) {
this.isRuning = false;
Release.reslese(dis, client);
}
}
private String recieve() {
String msg ="";
try {
msg = dis.readUTF();
} catch (IOException e) {
Release.reslese(dis);
}
return msg;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(isRuning){
String msg = recieve();
if(!"".equals(msg))
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
}
|
3. 释放资源
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| package chatVersion;
import java.io.Closeable;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Release {
public static void reslese(Closeable... targets){
for(Closeable target: targets){
if(target != null){
try {
target.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
|
4. 运行效果