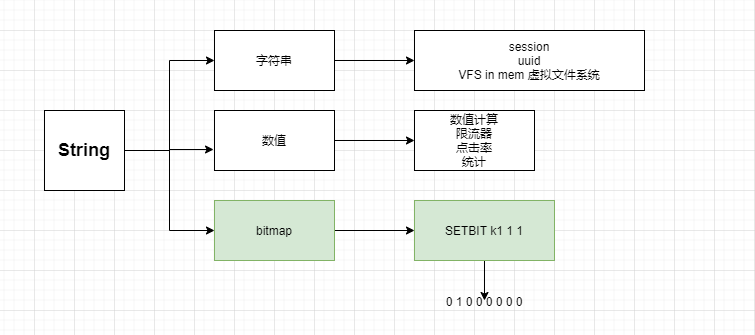
String 数据类型 字符串类型,也可以进行数值计算,bitmap也属于String。
1 2 3 4 127.0.0.1:6379> set a hello OK 127.0.0.1:6379> get a "hello"
String类型的数据结构存储方式有三种int、raw、embstr。那么这三种存储方式有什么区别
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 127.0.0.1:6379> set k1 345 OK 127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding k1 "int" 127.0.0.1:6379> set k2 3.2000 OK 127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding k2 "embstr" 127.0.0.1:6379>
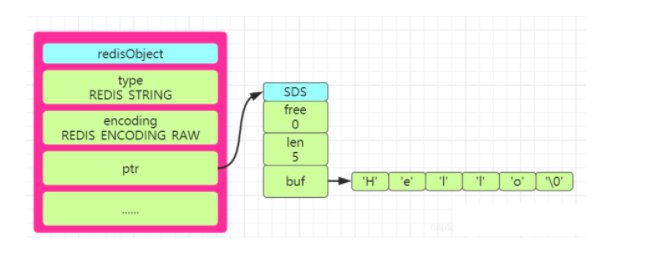
Redis中规定假如存储的是整数型值 ,比如set num 123这样的类型,就会使用 int的存储方式进行存储,在redisObject的ptr属性 中就会保存该值。
假如存储的字符串是一个字符串值并且长度大于32个字节 就会使用SDS(simple dynamic string)方式进行存储,并且encoding设置为raw;若是字符串长度小于等于32个字节 就会将encoding改为embstr来保存字符串.
SDS称为简单动态字符串 ,对于SDS中的定义在Redis的源码中有的三个属性int len、int free、char buf[]。 len保存了字符串的长度,free表示buf数组中未使用的字节数量,buf数组则是保存字符串的每一个字符元素。
SDS与C语言字符串有什么区别呢?
Redis没有使用C语言的字符串,而是自己定义和设计了自己的字符串类型,具有很多优势、
C语言的字符串类型没有len属性,如果要获得字符串的长度只能遍历一遍去统计,时间复杂度为O(n)。而Redis中的SDS有len这个属性,直接返回len值就行,时复为O(1)。
C语言两个字符串拼接如果没有分配足够长度的空间的话,会出现缓冲区溢出的情况。而redis会先根据 len的属性判断空间是否满足要求,空间不够时会相应扩展,不会缓冲区溢出。
具体的空间预分配原则是:当修改字符串后的长度len小于1MB,就会预分配和len一样长度的空间,即len=free;若是len大于1MB,free分配的空间大小就为1MB 。
SDS有空间预分配和惰性空间释放两种策略。在为字符串分配空间的时候,分配的空间比实际要多。能减少连续的执行字符串增长带来内存重新分配的次数 。
当字符串被缩短 的时候,SDS也不会立即回收不适用的空间,而是通过free属性将不使用的空间记录下来,等后面使用的时候再释放。
SDS是二进制安全的,除了可以储存字符串以外还可以储存二进制文件(如图片、音频,视频等文件的二进制数据);而c语言中的字符串是以空字符串作为结束符,一些图片中含有结束符,因此不是二进制安全的。
c语言字符串 SDS 获取长度的时间复杂度为O(n) 获取长度的时间复杂度为O(1) 不是二进制安全的 是二进制安全的 只能保存字符串 还可以保存二进制数据 n次增长字符串必然会带来n次的内存分配 n次增长字符串内存分配的次数<=n
VFS 虚拟文件系统 1 2 3 4 5 127.0.0.1:6379> set /root/user/video a.ma4 OK 127.0.0.1:6379> get /root/user/video "a.ma4"
数值计算 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 127.0.0.1:6379> set k1 4 OK 127.0.0.1:6379> DECR k1 (integer ) 3 127.0.0.1:6379> get k1 "3" 127.0.0.1:6379> INCRBY k1 5 (integer ) 8 127.0.0.1:6379> get k1 "8"
strlen 计算的是字节数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 127.0.0.1:6379> set k1 a OK 127.0.0.1:6379> STRLEN a (integer ) 0 127.0.0.1:6379> STRLEN k1 (integer ) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> APPEND k1 xxoo (integer ) 5 127.0.0.1:6379> STRLEN k1 (integer ) 5 127.0.0.1:6379> APPEND k1 朱 (integer ) 8 127.0.0.1:6379> get k1 "axxoo\xe6\x9c\xb1" 127.0.0.1:6379> strlen k1 (integer ) 8
bitmap 是一个二进制位
1 2 3 4 127.0.0.1:6379> SETBIT k1 1 1 (integer ) 0 127.0.0.1:6379> get k1 "@"
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 127.0.0.1:6379> SETBIT k1 7 1 (integer ) 0 127.0.0.1:6379> get k1 "A" 127.0.0.1:6379> SETBIT k2 1 1 (integer ) 0 127.0.0.1:6379> SETBIT k2 6 1 (integer ) 0 127.0.0.1:6379> get k2 "B"
与或操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 127.0.0.1:6379> BITOP and andkey k1 k2 (integer ) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> get andkey "@" 127.0.0.1:6379> BITOP or orkey k1 k2 (integer ) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> get orkey "C"
如果设置的位数很大,会自动进行字节拓宽
1 2 3 4 5 6 127.0.0.1:6379> SETBIT k1 9999 1 (integer ) 0 127.0.0.1:6379> STRLEN k1 (integer ) 1250 127.0.0.1:6379>
bitcount统计1的个数 1 2 3 4 127.0.0.1:6379> BITCOUNT k1 0 0 (integer ) 2 127.0.0.1:6379> BITCOUNT k1 0 -1 (integer ) 3
bitmap的应用场景 用户统计 需求: 统计任意时间窗 统计用户的登录天数
使用bitmap来做。
比如统计一年内用户的登录天数,可以创建一个365位的bitmap,用户在哪一天登陆了,就将对应的位置为1,然后使用bitcount来统计1的个数,即为用户的登录总天数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 127.0.0.1:6379> SETBIT hongliang 2 1 (integer ) 0 127.0.0.1:6379> SETBIT hongliang 364 1 (integer ) 0 127.0.0.1:6379> BITCOUNT hongliang 0 -1 (integer ) 2
1 2 127.0.0.1:6379> STRLEN hongliang (integer ) 46
京东618只要用户登录就送一个礼物 假设京东有2个亿个用户,那么我们需要准备多少份礼物。
用户分为活跃用户和僵尸用户,我们应该为活跃用户准备礼物。
1 2 3 4 5 6 127.0.0.1:6379> SETBIT 20200101 2 1 (integer ) 0 127.0.0.1:6379> SETBIT 20200101 6 1 (integer ) 0 127.0.0.1:6379> SETBIT 20200102 6 1 (integer ) 0
这样设计,我们可以看出, 1月1日和1月2日两天只有两个用户登陆了,我们可以使用或运算来得出2.
1 2 3 4 127.0.0.1:6379> BITOP or res 20200101 20200102 (integer ) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> BITCOUNT res 0 -1 (integer ) 2
12306 12306买票问题
将座位的情况缓存到redis中,每一个站的座位情况使用bitmap来处理。
假如客户P买了从A-B的车票,客户Q想买A-D的车票,那么只需要将ABCD四个站的bitmap进行或运算即可,为0的那个座位才能买。
linux权限管理 chmod 777
rwx rwx rwx 持有者 持有组 其他人 任何人都有权限
三个位分别表示421
000 = 0
111= 7
List Redis中的列表在3.2之前的版本是使用ziplist和linkedlist进行实现的。在3.2之后的版本就是引入了quicklist。
linkedlist是一个双向链表。quicklist底层也是采用链表实现的。
Redis中链表的特性:
每一个节点都有指向前一个节点和后一个节点的指针。 头节点和尾节点的prev和next指针指向为null,所以链表是无环的。 链表有自己长度的信息,获取长度的时间复杂度为O(1)。 数据结构使用 lpush 队列
rpop 栈
LinkedList 双向链表
lindex 数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH k1 a b c d e (integer ) 5 127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE k1 0 -1 1) "e" 2) "d" 3) "c" 4) "b" 5) "a" 127.0.0.1:6379> LINDEX k1 2 "c" 127.0.0.1:6379> rpush k1 x y z (integer ) 8 127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE k1 0 -1 1) "e" 2) "d" 3) "c" 4) "b" 5) "a" 6) "x" 7) "y" 8) "z" 127.0.0.1:6379> rpop k1 "z"
ltrim 保留数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE k1 0 -1 1) "e" 2) "d" 3) "c" 4) "b" 5) "a" 6) "x" 7) "y" 8) "z" 127.0.0.1:6379> rpop k1 "z" 127.0.0.1:6379> LTRIM k1 0 3 OK 127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE k1 0 -1 1) "e" 2) "d" 3) "c" 4) "b"
应用场景 阻塞队列 结合lpush和brpop命令就可以实现。生产者使用lupsh从列表的左侧插入元素,消费者使用brpop命令从队列的右侧获取元素进行消费。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 package cn.hongliang.redismessage.config;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisStandaloneConfiguration;import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig;@Configuration public class RedisConfig @Value("${spring.redis.host}") private String host; @Value("${spring.redis.port}") private int port; @Value("${spring.redis.pool.max-active}") private int maxActive; @Value("${spring.redis.pool.max-idle}") private int maxIdle; @Value("${spring.redis.pool.min-idle}") private int minIdle; @Value("${spring.redis.pool.max-wait}") private int maxWait; @Value("${spring.redis.database}") private int database; @Value("${spring.redis.timeout}") private int timeout; @Bean public JedisPoolConfig getRedisConfiguration () JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig(); jedisPoolConfig.setMaxTotal(maxActive); jedisPoolConfig.setMaxIdle(maxIdle); jedisPoolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(maxWait); return jedisPoolConfig; } @Bean public JedisConnectionFactory getRedisConnectionFactory () RedisStandaloneConfiguration redisStandaloneConfiguration = new RedisStandaloneConfiguration(); redisStandaloneConfiguration.setHostName(host); redisStandaloneConfiguration.setPort(port); redisStandaloneConfiguration.setDatabase(database); JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig= getRedisConfiguration(); JedisConnectionFactory factory = new JedisConnectionFactory(redisStandaloneConfiguration); factory.setPoolConfig(jedisPoolConfig); return factory; } @Bean public RedisTemplate<?, ?> getRedisTemplate() { JedisConnectionFactory factory = getRedisConnectionFactory(); RedisTemplate<?, ?> redisTemplate = new StringRedisTemplate(factory); return redisTemplate; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 package cn.hongliang.utils;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import java.util.List;@Component public class RedisUtil @Autowired private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate; public boolean lPushMessage (String key, Object value) try { redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(key, value); return true ; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return false ; } } public Object rPopMessage (String key) try { return redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPop(key); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return null ; } } public List<Object> getMessage (String key, long start, long end) try { return redisTemplate.opsForList().range(key, start, end); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return null ; } } }
Hash Hash对象的实现方式有两种,分别是ziplist、hashtable;
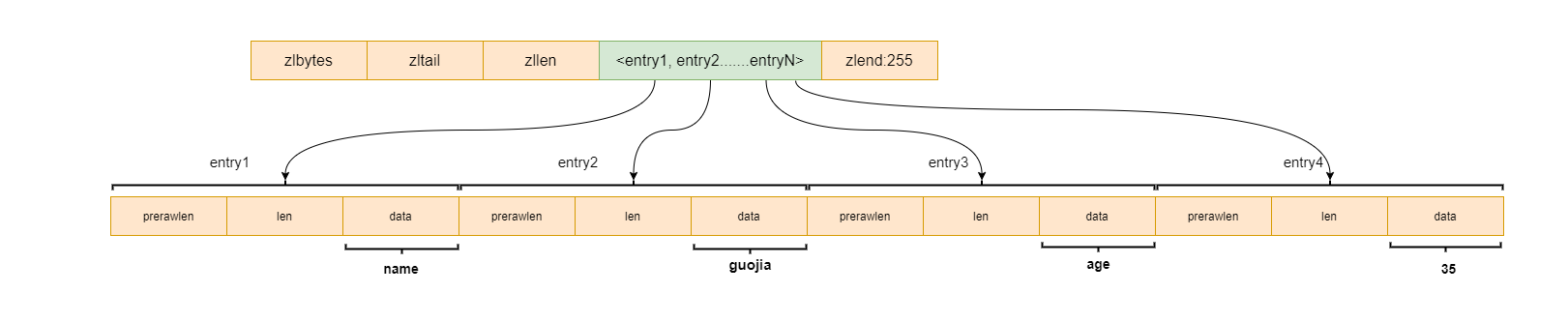
ziplist 压缩列表(ziplist)是一组连续内存块组成的顺序的数据结构,压缩列表能够节省空间,压缩列表中使用多个节点来存储数据。
压缩列表是列表键和哈希键底层实现的原理之一,压缩列表并不是以某种压缩算法进行压缩存储数据,而是它表示一组连续的内存空间的使用,节省空间 ,压缩列表的内存结构图如下:
压缩列表中每一个节点表示的含义如下所示:
zlbytes:4个字节的大小,记录压缩列表占用内存的字节数。zltail:4个字节大小,记录表尾节点距离起始地址的偏移量,用于快速定位到尾节点的地址。zllen:2个字节的大小,记录压缩列表中的节点数。entry:表示列表中的每一个节点。zlend:表示压缩列表的特殊结束符号'0xFF'。再压缩列表中每一个entry节点又有三部分组成,包括previous_entry_ength、encoding、content。
previous_entry_ength表示前一个节点entry的长度,可用于计算前一个节点的其实地址,因为他们的地址是连续的。encoding:这里保存的是content的内容类型和长度。 content:content保存的是每一个节点的内容。 用法类似HashMap 类似HashMap, 用法如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 help @hash HDEL key field [field ...] summary: Delete one or more hash fields since: 2.0.0 HEXISTS key field summary: Determine if a hash field exists since: 2.0.0 HGET key field summary: Get the value of a hash field since: 2.0.0 HGETALL key summary: Get all the fields and values in a hash since: 2.0.0 HINCRBY key field increment summary: Increment the integer value of a hash field by the given number since: 2.0.0 HINCRBYFLOAT key field increment summary: Increment the float value of a hash field by the given amount since: 2.6.0 HKEYS key summary: Get all the fields in a hash since: 2.0.0 HLEN key summary: Get the number of fields in a hash since: 2.0.0 HMGET key field [field ...] summary: Get the values of all the given hash fields since: 2.0.0 HMSET key field value [field value ...] summary: Set multiple hash fields to multiple values since: 2.0.0 HSCAN key cursor [MATCH pattern] [COUNT count] summary: Incrementally iterate hash fields and associated values since: 2.8.0 HSET key field value summary: Set the string value of a hash field since: 2.0.0 HSETNX key field value summary: Set the value of a hash field, only if the field does not exist since: 2.0.0 HSTRLEN key field summary: Get the length of the value of a hash field since: 3.2.0 HVALS key summary: Get all the values in a hash since: 2.0.0
设置和获取数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 127.0.0.1:6379> hset k1 name tom (integer ) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> HSET k1 age 12 (integer ) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> keys * 1) "k1" 127.0.0.1:6379> HVALS k1 1) "tom" 2) "12" 127.0.0.1:6379> HKEYS k1 1) "name" 2) "age" 127.0.0.1:6379> HGET k1 name "tom" 127.0.0.1:6379> HGET k1 age "12" 127.0.0.1:6379> HINCRBY k1 age 3 (integer ) 15 127.0.0.1:6379> HVALS k1 1) "tom" 2) "15"
应用场景 商品详情页 聚合场景 用户数据管理 存储用户的信息: 用户id作为key,其他信息作为value hash也可以用作高并发场景下使用Redis生成唯一的id。 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public Long getId (String key,String hashKey,Long offset) throws BusinessException try { if (null == offset) { offset=1L ; } return redisUtil.increment(key, hashKey, offset); } catch (Exception e) { int randNo=UUID.randomUUID().toString().hashCode(); if (randNo < 0 ) { randNo=-randNo; } return Long.valueOf(String.format("%16d" , randNo)); } }
Set 是一个无序的集合,不允许添加重复元素。 Set的底层实现是ht和intset ,ht(哈希表)前面已经详细了解过,下面我们来看看intset类型的存储结构。
intset也叫做整数集合,用于保存整数值的数据结构类型,它可以保存int16_t、int32_t 或者int64_t 的整数值。
在整数集合中,有三个属性值encoding、length、contents[],分别表示编码方式、整数集合的长度、以及元素内容,length就是记录contents里面的大小。
在整数集合新增元素的时候,若是超出了原集合的长度大小,就会对集合进行升级,具体的升级过程如下:
首先扩展底层数组的大小,并且数组的类型为新元素的类型。 然后将原来的数组中的元素转为新元素的类型,并放到扩展后数组对应的位置。 整数集合升级后就不会再降级,编码会一直保持升级后的状态。 无序去重 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 127.0.0.1:6379> sadd k1 a b c d a c (integer ) 4 127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS k1 1) "a" 2) "c" 3) "b" 4) "d" 127.0.0.1:6379>
SRANDMEMBER随机返回元素 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER k1 2 1) "b" 2) "c" 127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER k1 4 1) "d" 2) "a" 3) "b" 4) "c"
返回的是一个集合,如果是正数,则返回的是一个不重复的集合,如果是负数,则可能会返回重复的集合。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER k1 -3 1) "b" 2) "c" 3) "b" 127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER k1 -3 1) "d" 2) "b" 3) "d" 127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER k1 -3 1) "b" 2) "b" 3) "a" 127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER k1 -3 1) "d" 2) "b" 3) "a" 127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER k1 -8 1) "c" 2) "a" 3) "b" 4) "d" 5) "b" 6) "d" 7) "a" 8) "d"
应用场景 抽奖
随机事件
并查集(共同好友)
推荐系统
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 127.0.0.1:6379> SADD k1 a b c d e (integer ) 5 127.0.0.1:6379> SADD k2 b f c d r (integer ) 5 127.0.0.1:6379> SUNION k1 k2 1) "r" 2) "c" 3) "b" 4) "d" 5) "f" 6) "a" 7) "e" 127.0.0.1:6379> SINTER k1 k2 1) "d" 2) "c" 3) "b" 127.0.0.1:6379> SDIFF k1 k2 1) "a" 2) "e" 127.0.0.1:6379> SDIFF k2 k1 1) "f" 2) "r"
Zset 有序集合,通过score来排序。 ZSet的底层实现是ziplist和skiplist
skiplist也叫做跳跃表 ,跳跃表是一种有序的数据结构,它通过每一个节点维持多个指向其它节点的指针,从而达到快速访问的目的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 BZPOPMAX key [key ...] timeout summary: Remove and return the member with the highest score from one or more sorted sets, or block until one is available since: 5.0.0 BZPOPMIN key [key ...] timeout summary: Remove and return the member with the lowest score from one or more sorted sets, or block until one is available since: 5.0.0 ZADD key [NX|XX] [CH] [INCR] score member [score member ...] summary: Add one or more members to a sorted set , or update its score if it already exists since: 1.2.0 ZCARD key summary: Get the number of members in a sorted set since: 1.2.0 ZCOUNT key min max summary: Count the members in a sorted set with scores within the given values since: 2.0.0 ZINCRBY key increment member summary: Increment the score of a member in a sorted set since: 1.2.0 ZINTERSTORE destination numkeys key [key ...] [WEIGHTS weight] [AGGREGATE SUM|MIN|MAX] summary: Intersect multiple sorted sets and store the resulting sorted set in a new key since: 2.0.0 ZLEXCOUNT key min max summary: Count the number of members in a sorted set between a given lexicographical range since: 2.8.9 ZPOPMAX key [count] summary: Remove and return members with the highest scores in a sorted set since: 5.0.0 ZPOPMIN key [count] summary: Remove and return members with the lowest scores in a sorted set since: 5.0.0 ZRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES] summary: Return a range of members in a sorted set , by index since: 1.2.0 ZRANGEBYLEX key min max [LIMIT offset count] summary: Return a range of members in a sorted set , by lexicographical range since: 2.8.9 ZRANGEBYSCORE key min max [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT offset count] summary: Return a range of members in a sorted set , by score since: 1.0.5 ZRANK key member summary: Determine the index of a member in a sorted set since: 2.0.0 ZREM key member [member ...] summary: Remove one or more members from a sorted set since: 1.2.0 ZREMRANGEBYLEX key min max summary: Remove all members in a sorted set between the given lexicographical range since: 2.8.9 ZREMRANGEBYRANK key start stop summary: Remove all members in a sorted set within the given indexes since: 2.0.0 ZREMRANGEBYSCORE key min max summary: Remove all members in a sorted set within the given scores since: 1.2.0 ZREVRANGE key start stop [WITHSCORES] summary: Return a range of members in a sorted set , by index, with scores ordered from high to low since: 1.2.0 ZREVRANGEBYLEX key max min [LIMIT offset count] summary: Return a range of members in a sorted set , by lexicographical range, ordered from higher to lower strings. since: 2.8.9 ZREVRANGEBYSCORE key max min [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT offset count] summary: Return a range of members in a sorted set , by score, with scores ordered from high to low since: 2.2.0 ZREVRANK key member summary: Determine the index of a member in a sorted set , with scores ordered from high to low since: 2.0.0 ZSCAN key cursor [MATCH pattern] [COUNT count] summary: Incrementally iterate sorted sets elements and associated scores since: 2.8.0 ZSCORE key member summary: Get the score associated with the given member in a sorted set since: 1.2.0 ZUNIONSTORE destination numkeys key [key ...] [WEIGHTS weight] [AGGREGATE SUM|MIN|MAX] summary: Add multiple sorted sets and store the resulting sorted set in a new key since: 2.0.0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 127.0.0.1:6379> ZADD k1 4 apple 3.2 banana 1.6 orange (integer ) 3 127.0.0.1:6379> ZRANGE k1 0 -1 withscores 1) "orange" 2) "1.6000000000000001" 3) "banana" 4) "3.2000000000000002" 5) "apple" 6) "4" 127.0.0.1:6379> ZRANGE k1 0 -1 1) "orange" 2) "banana" 3) "apple"
排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 127.0.0.1:6379> ZREVRANGE k1 0 -1 withscores 1) "apple" 2) "4" 3) "banana" 4) "3.2000000000000002" 5) "orange" 6) "1.600000000000000
场景 排行榜 动态的排行榜。
有序事件 评论+分页 底层结构 跳跃表
1 2 3 4 127.0.0.1:6379> type k1 zset 127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT encoding k1 "ziplist"
可以看到并不是我们所说的跳表,而是一个list,这是因为我们的元素比较少。
如果我们的元素数量很多或者某个元素的值很大的话,则会使用跳表。
1 2 3 4 5 6 127.0.0.1:6379> ZADD k1 99 saddddddddkakjfhkashfkaskfhkahsfkjahkjfawoiffahkfnakshfakkshfffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffaoifafskaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa (integer ) 1 127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT encoding k1 "skiplist"
参考 一不小心肝出了4W字的Redis面试教程