描述
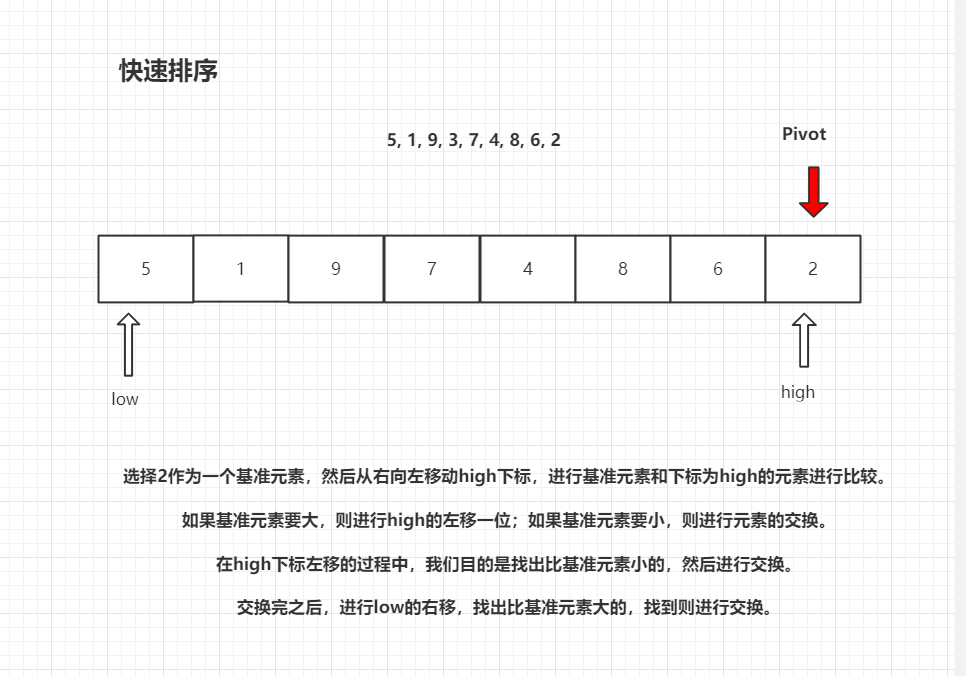
快速排序
快速排序的思想是,通过一趟排序将待排记录分割成独立的两部分,其中一部分记录的关键字均比另一部分记录的关键字小,则可分别对这两部分记录继续进行排序,以达到整个序列有序的目的。
快速排序之所以快,是因为它使用了分治法。它虽然也是通过不断的比较和移动来实现排序的,只不过它的实现,增大了比较的距离和移动的距离。而冒泡排序只是相邻的比较和交换。
1 | package Sort.QuickSort; |
经典快排和数据的状态有关:当然上述代码是经过优化了
- 当数据是极端情况,比如:
9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1。 选择最后一个元素为轴枢,会发现,每一个元素都比轴枢大,进行一次快速排序之后,最后会将轴枢放在第一位,复杂度都是:$O(N^2)$ .
上面代码减少了不必要的交换,即将轴枢保存了下来, 不用每次都交换,在最终确定位置的时候再交换。
进一步优化: 我们都知道,递归对性能是有一定影响的,quickSort函数尾部有两次递归操作。如果待排序的序列极为极端不平衡,递归的深度几乎接近于n的高度(没有了二分法的优势)。这样的时间复杂度也是达到了最坏的程度$ O (N^2) $ ,而不是平衡时的$O(nlogn)$。
时间慢也就算了,但是栈的大小也是有限的,每次递归操作都消耗一定的栈空间,函数的参数越多,每次递归调用参数耗费的空间也是越多。
如果能减少递归,性能也因此大大提高:
1 | public void quickSort(int[] arrs, int low, int high) { |
这是一个很好的方法。我们把if改成while,然后一次递归之后,左边的部门已经排好序了,low已经没有用处了,所以把pivot+1赋值给low作为下一个参数, 对右半部分排序,减少了一半的递归程度。
因此采用迭代而不是递归的方法可以缩减堆栈深度,从而提高了整体性能。
荷兰国旗问题一
其实荷兰国旗问题就是一个数组划分的问题
给定一个数组arr,和一个数num,请把小于等于num的数放在数组的左边,大于num的数放在数组的右边。 要求额外空间复杂度O(1),时间复杂度O(N)。
分析
很明显这就是快速排序的一次划分的过程,只不过轴枢是给定的一个数。
代码
1 | package Sort.QuickSort; |
荷兰国旗问题二
给定一个数组arr,和一个数num,请把小于num的数放在数组的左边,等于num的数放在数组的中间,大于num的数放在数组的右边。 要求额外空间复杂度O(1),时间复杂度O(N) 。
这题与上面的题目区别是,这个题目是要将数组划分成三个部分,大于部分,等于部分,小于部分。
参照快速排序代码,很容易解出来。直接看代码就懂了。
1 | package Sort.QuickSort; |
1 2 3 4 2 6 6 6 9 10 8 12
小于的区域:
1 2 3 4 2
等于的区域:
6 6 6
大于的区域:
9 10 8 12


